The Menopause Maze: Important Facts About The Symptoms

Last Updated on June 30, 2025 by George
Menopause comes with its own set of signals, such as unpredictable periods, intense hot flashes, night sweats, swings in mood, and shifts in sexual interest. These signs are the body’s way of adapting to lower levels of estrogen and progesterone.
Recent research has revolutionized our understanding of menopause treatment options. The latest findings show that hormone therapy is safer than previously believed for women under 60, offering relief for bothersome symptoms without the exaggerated risks once feared. Beyond hormones, you’ll explore lifestyle modifications, alternative therapies, and non-hormonal treatments that can significantly improve your quality of life.
Whether you’re just beginning to notice changes or you’re deep in the menopause transition, this article provides practical insights into recognizing symptoms, understanding your treatment options, and taking control of your health. You’ll learn how to work effectively with your healthcare provider and discover actionable strategies for managing everything from night sweats to mood changes.
Ready to turn uncertainty into empowerment? Let’s explore how you can embrace this life stage with wisdom and well-being as your guides.
Everything You Need to Know About Menopause
Navigating through this significant life transition, women encounter a milestone that deserves understanding, respect, and proper care. Menopause marks the natural end of reproductive years, typically occurring in a woman’s late 40s to early 50s, though every woman’s experience unfolds uniquely.
Prefer to listen rather than read?
Menopause also brings a hike in the risk of osteoporosis, heart disease, and urinary incontinence. By understanding these risks, women can get ahead of them. Actions like keeping active, eating right, and talking over prevention with their doctor can make a big difference.
Understanding menopause and perimenopause is crucial for women, as it can help them prepare for the changes that are coming and manage the symptoms that may arise. Navigating this transition with knowledge and confidence can also help women maintain their overall health and well-being.
Understanding the signs and symptoms becomes crucial for managing this phase with grace and confidence as your body signals important hormonal changes ahead.
Perimenopause Period
Before menopause officially begins, most women experience perimenopause—a transitional period that typically starts in the 40s but can begin earlier or later. This phase can extend for several years and brings its own unique considerations.
During perimenopause, your ovaries gradually reduce estrogen production, leading to irregular periods that may become heavier, lighter, longer, or shorter than before. Some women notice spotting between periods, which, while often normal during this transition, should still be discussed with your healthcare provider.
Beyond menstrual changes, perimenopause can introduce you to symptoms you’ll recognize throughout the menopause journey: temperature fluctuations, sleep disruptions, mood changes, and physical discomfort.

Common Signs and Symptoms
While every woman’s experience differs, certain symptoms appear frequently during the menopause transition. Understanding these changes helps you recognize what’s happening and seek appropriate support when needed.
These are the most common ones include:
Irregular Periods
As menopause approaches, changing hormone levels affect your menstrual cycle in various ways. You might experience longer or shorter cycles, heavier or lighter bleeding, or completely missed periods. Some women notice spotting between periods.
These irregularities reflect the natural fluctuation of estrogen and progesterone as your reproductive system transitions. However, any unexpected bleeding patterns warrant discussion with your healthcare provider to rule out other conditions.
Hot Flashes
Research shows that hot flashes affect up to 80% of women during menopause, making them one of the most common experiences of this transition. These sudden waves of warmth typically begin in the chest and spread to the neck, face, and arms, often accompanied by sweating and skin flushing.
Hot flashes can last from seconds to several minutes and may occur multiple times daily or just occasionally. The intensity varies greatly—some women experience mild warmth while others face intense heat that disrupts daily activities. Some women continue experiencing hot flashes for several years after menopause.
Night Sweats
Affecting approximately 75% of women during menopause, night sweats are essentially hot flashes that occur during sleep. These episodes can wake you feeling damp or completely soaked, often accompanied by fatigue, restlessness, and anxiety the following day.
Night sweats happen when hormonal changes confuse your body’s temperature regulation system. As estrogen levels decline, your hypothalamus—your internal thermostat—becomes more sensitive and may trigger cooling responses even when you’re not actually overheated.
Physical Comfort Changes
Declining estrogen levels affect the tissues throughout your body, particularly in intimate areas. Vaginal tissues may become thinner, drier, and less elastic—a condition called genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM).
These changes can cause discomfort, itching, burning, or pain during intimate moments. Additionally, the tissue changes may increase susceptibility to urinary tract infections, as thinner tissues provide less natural protection against bacteria.
Mood and Emotional Changes
The hormonal fluctuations during menopause can significantly impact your emotional well-being. You might experience mood swings, increased irritability, anxiety, or feelings of sadness that seem to appear without clear triggers.
These emotional changes result from hormonal effects on brain neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which help regulate mood. Additionally, the life transitions that often accompany menopause—such as children leaving home or career changes—can contribute to emotional challenges.
Sleep Disruptions
Many women find their sleep patterns changing during menopause. You might have trouble falling asleep, staying asleep, or both. These disruptions often stem from hot flashes and night sweats, but hormonal changes can also directly affect sleep quality.
Poor sleep can create a cycle of challenges, contributing to mood changes, fatigue, and difficulty managing other menopause symptoms.

Changes in Intimacy
Some women notice decreased interest in intimate relationships or difficulty reaching satisfaction during menopause. These changes result from multiple factors: declining estrogen affects blood flow to intimate areas, while decreasing testosterone levels can impact desire and response.
Physical discomfort from tissue changes can make intimacy less appealing, creating emotional impacts that further affect intimate relationships.
Urinary Changes
Estrogen helps maintain the health and strength of urinary tract tissues. As levels decline, you might experience urinary incontinence, particularly stress incontinence that occurs with physical activity, coughing, or sneezing.
Frequent urination, especially at night, is also common. Some women notice increased susceptibility to urinary tract infections due to tissue changes that make bacterial growth easier.

What are the Treatment Options
Menopause is a natural part of a woman’s life, but the symptoms that come with it can be quite challenging to deal with. The good news is that there are several treatment options available that can make this transition a lot smoother. While some women may be hesitant to seek treatment, they should consider it. There are several treatment options available for menopause, depending on the individual’s symptoms and overall health.
Here are some of the most common treatments:
Hormone Therapy (HT)
Modern hormone therapy replaces the estrogen and progesterone your body produces less of during menopause. Available in various forms—pills, patches, creams, gels, or vaginal rings—hormone therapy can effectively relieve hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal discomfort, and mood fluctuations.
Current research shows hormone therapy is relatively safe for short-term treatment of menopause symptoms in women under 60. Your healthcare provider can help determine if hormone therapy suits your individual health profile and risk factors.
Non-Hormonal Treatments
Several non-hormonal medications have proven effective for managing menopause symptoms. Certain antidepressants, anti-seizure medications, and blood pressure medications can reduce hot flashes and mood-related symptoms.
These medications work by affecting brain neurotransmitters involved in temperature regulation and mood control. While they may have potential side effects, they offer valuable alternatives for women who cannot or prefer not to use hormone therapy.
Vaginal Estrogen
Vaginal estrogen therapy specifically addresses intimate discomfort without significantly affecting your overall estrogen levels. Available as creams, tablets, or rings, these treatments help restore tissue health and comfort.
This localized approach provides relief from dryness, discomfort, and increased infection risk while minimizing systemic hormone exposure. Most women can safely use vaginal estrogen, though you should discuss your individual situation with your healthcare provider.
While vaginal estrogen is generally considered safe and effective, it is important to talk to a healthcare provider before starting any new medication or hormone therapy. This is especially true for women who have a history of breast cancer, as estrogen can sometimes promote the growth of certain types of breast cancer cells. However, for most women, vaginal estrogen is a safe and effective option for managing the symptoms of vaginal dryness and discomfort. In regards to breast cancer, early detection is always a viable option.
Lifestyle Changes
Strategic lifestyle changes can significantly impact your menopause experience. Managing hot flash triggers helps many women reduce symptom frequency and severity. Common triggers include caffeine, alcohol, spicy foods, hot beverages, and stressful situations.
Staying cool through appropriate clothing choices, fans, air conditioning, and cool beverages helps manage temperature-related symptoms. Regular physical activity supports overall well-being and can reduce symptom intensity.
Stress management techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or other relaxation practices can help manage both physical symptoms and emotional challenges.
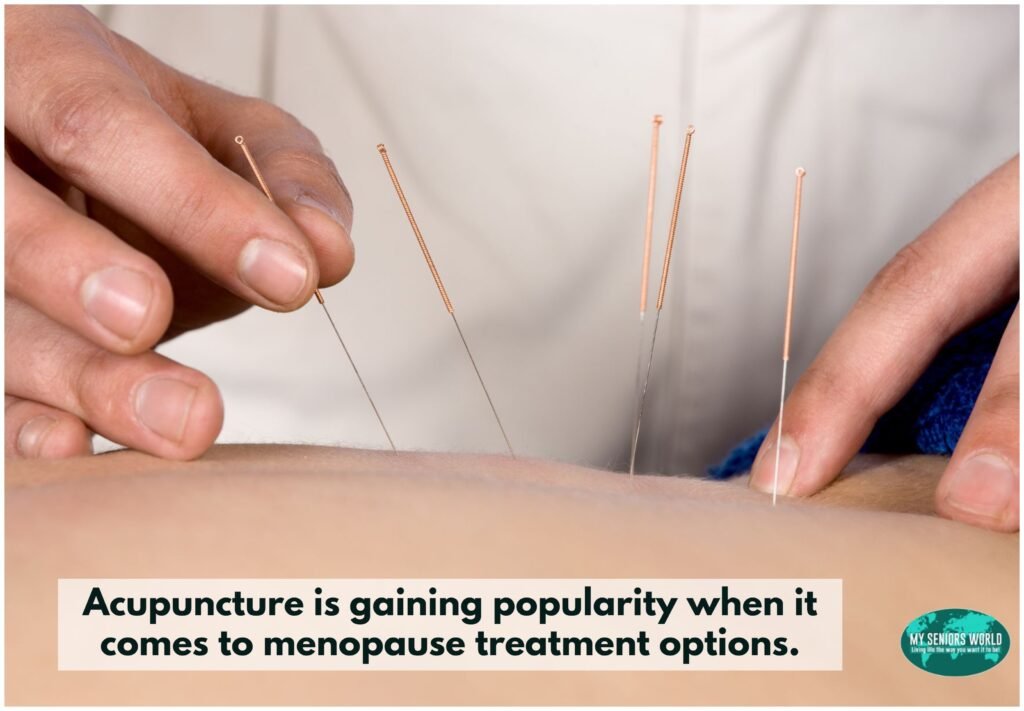
Alternative Therapies
Many women explore complementary therapies to support their menopause journey. Acupuncture shows promise for reducing hot flashes in some studies, though more research continues to evaluate its effectiveness.
Certain herbal supplements, including black cohosh, soy isoflavones, and red clover, have been used for symptom management. However, these supplements aren’t regulated by the FDA and may interact with other medications or have unexpected effects.
Mind-body practices like yoga, meditation, and tai chi can improve overall well-being and may help manage symptoms while supporting emotional balance during this transition.
It’s important to remember that the treatment options for menopause vary depending on individual needs and preferences, and not all options may be suitable for everyone. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan for your individual needs.
Conclusion
Have you started noticing changes that might signal the beginning of your menopause journey? Are you currently managing symptoms and wondering about your options? We’d love to hear about your experiences, what approaches have you tried, and what questions do you still have? Share your thoughts and connect with other women navigating this important life transition by leaving a comment below.
Disclaimer
The content provided on MySeniors.World is for informational purposes only and is not intended as either financial or medical advice. Always consult a qualified professional before making any investment or health-related decisions.
Posts may contain affiliate links, meaning we earn a commission – at no additional cost to you, if you click through and make a purchase. Your support helps us continue providing valuable content.
Frequently Asked Questions About Menopause
- At what age does menopause typically begin?
- Most women experience menopause between ages 45-55, with the average age being 51. However, perimenopause often begins several years earlier, typically in the 40s. Some women experience earlier or later menopause due to genetics, medical treatments, or other factors.
- How long do menopause symptoms last?
- Symptoms vary greatly among women. Hot flashes and night sweats typically last 1-5 years, though some women experience them longer. Other symptoms like vaginal dryness may persist without treatment. The perimenopause transition usually lasts 2-8 years before periods stop completely.
- Is hormone therapy safe for everyone?
- Recent research shows hormone therapy is generally safe for healthy women under 60 who start treatment within 10 years of menopause. However, individual risk factors matter. Women with a history of blood clots, certain cancers, or heart disease may need alternative approaches. Always consult your healthcare provider about your specific situation.
- Can I still get pregnant during perimenopause?
- Yes, pregnancy remains possible during perimenopause until you’ve gone 12 consecutive months without a period. Even with irregular cycles, ovulation can still occur. If you don’t want to become pregnant, continue using contraception throughout perimenopause.
- What’s the difference between menopause and perimenopause?
- Perimenopause is the transitional period leading up to menopause when hormone levels fluctuate and symptoms begin. Menopause officially occurs after 12 consecutive months without menstrual periods. Postmenopause refers to the years following menopause.
- Do all women experience severe menopause symptoms?
- No, experiences vary widely. Some women have minimal symptoms, while others face significant challenges. About 20% of women experience severe symptoms that substantially impact daily life. Most women fall somewhere in between, with manageable symptoms that benefit from treatment.
- Are there natural ways to manage menopause symptoms?
- Yes, lifestyle modifications can help significantly. Regular exercise, stress management, avoiding known triggers (like caffeine or spicy foods), maintaining a cool environment, and practicing relaxation techniques all support symptom management. Some women also find relief with acupuncture or mind-body practices.
- When should I see a healthcare provider about menopause symptoms?
- Consult your provider if symptoms significantly impact your quality of life, if you experience unusual bleeding patterns, or if you’re interested in exploring treatment options. Don’t wait until symptoms become unbearable—early intervention often provides better outcomes.
REFERENCES
- The Menopause Society. (2024). Clinical guidelines and position statements. Retrieved from https://menopause.org/
- Manson, J. E. (2024). Long-term follow-up of hormone therapy safety in menopausal women. Brigham and Women’s Hospital study findings.
- International Menopause Society. (2024). White Paper on menopause and hormone therapy controversies. Climacteric, 27(3).
- Yang, H., & Toriola, A. T. (2024). Recent trends in menopausal hormone therapy use in the US. JAMA Health Forum.
- World Health Organization. (2024). Menopause fact sheet. Retrieved October 2024.
- National Library of Medicine. (2024). Hormones for menopause safety research findings.
- Nature Medicine. (2025). The new science of menopause: emerging therapies and research directions.






Responses