Last Updated on June 27, 2025 by Julian Espinosa
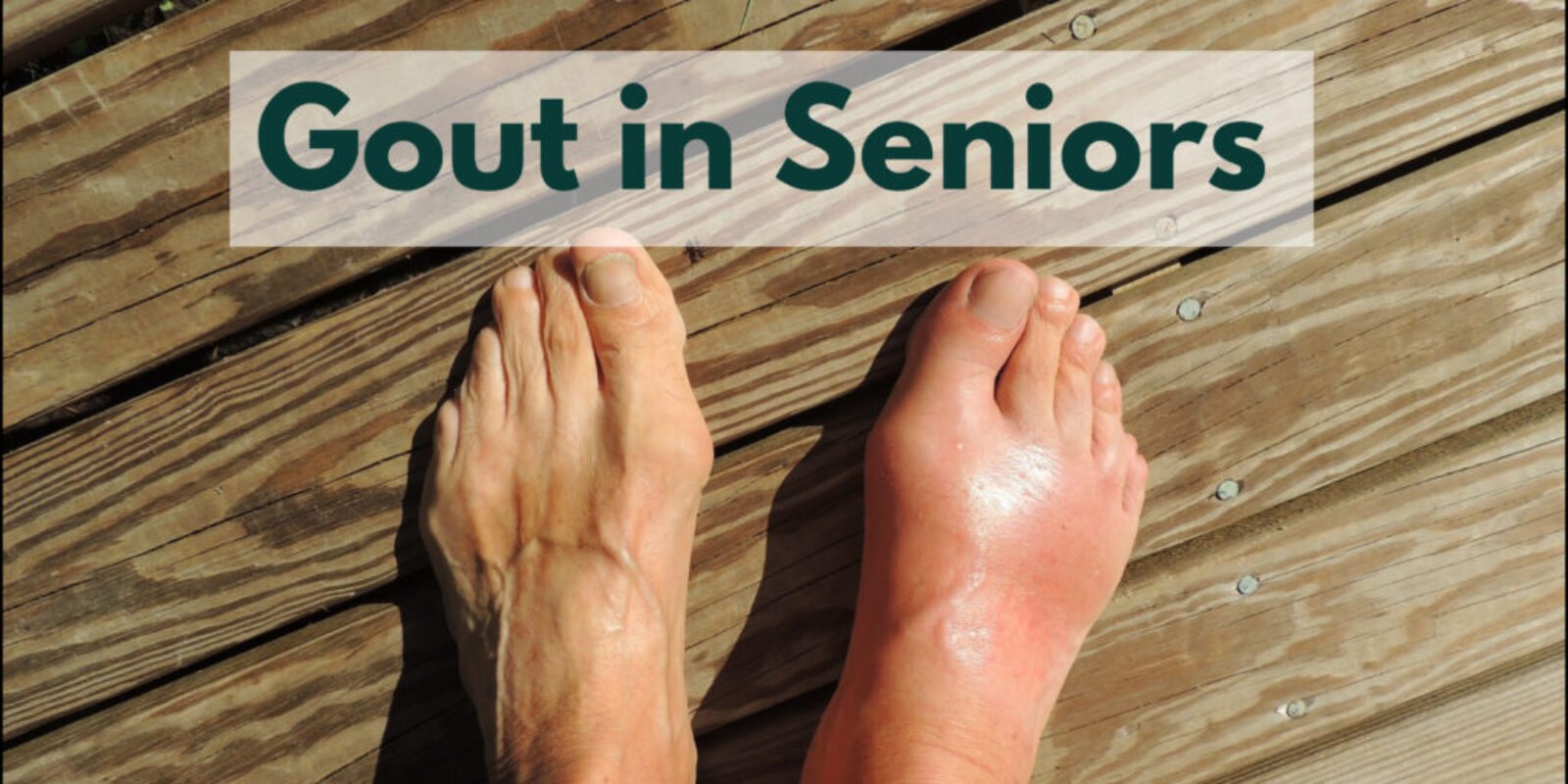
Gout is an inflammatory disease that causes extreme pain and discomfort to those afflicted. Too much uric acid in your bloodstream leads to a crystal-clear problem—literally! These crystals like to party at your joints, causing all sorts of trouble.
This crystallization leads to the formation of tophi, small deposits that can be visible on the skin and cause immense pain. While gout can affect people of any age, gout in seniors is more common due to the numerous risk factors associated with advanced age. Understandably, gout can be especially difficult to navigate in the elderly.
Gout in seniors can be managed with proper lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet and exercising regularly and in some cases, medication. Keep gout in check and pain at bay with the perfect treatment plan! With the right approach, living a vibrant, pain-free life is totally within reach.
What You Need to Know About Gout in Seniors!
Ready to kick gout to the curb? In this blog post, we’re spilling the beans on all things gout in seniors, and dishing out top-notch strategies to tackle those symptoms head-on! We’ll provide tips on lifestyle changes, medications, and dietary modifications to help those with gout in their senior years.
Additionally, we’ll explore the importance of seeking timely medical care for optimal gout management and prevention. Get in the know and take charge! Armed with the lowdown on risk factors, complications, and treatments, seniors can power up their quality of life and live it up!

Prefer to listen rather than read?
Understanding the Symptoms of Gout
Gout in the elderly? It’s a real pain, but don’t sweat it! This common arthritis type brings the heat with joint pain and swelling, but fear not—we’ve got the tricks to tackle it head-on!
Take a look at these indicators of gout in seniors to make sure we’re keeping our elderly loved ones healthy!
Pain in joints
- Symptoms of gout in seniors include sudden, severe pain in joints, often in the toes or ankles, and the affected area. The pain can be so intense that even the lightest of touches can be unbearable.
Redness, Tenderness and Swelling in the Affected Joint
- Redness, tenderness, and swelling in the joint scream gout—a fiery form of arthritis that means business!
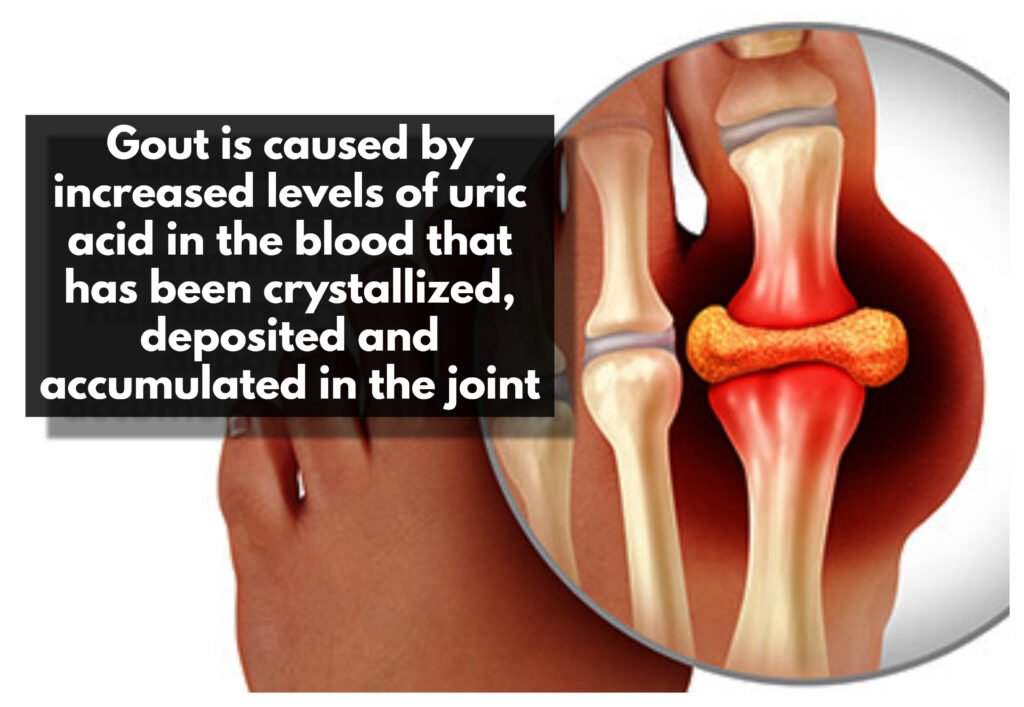
- The redness is caused by increased blood flow to the area, while the tenderness is caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals around the joint, leading to pain and discomfort.
- Swelling is caused by the accumulation of fluid around the joint, which can cause pressure and stiffness.
Inflammation
- This is due to the accumulation of uric acid crystals which irritate the joint and cause inflammation and swelling.
- This inflammation of the joint can cause it to become stiff and difficult to move and can cause severe pain when attempting to move the joint.
Burning sensation in the affected joint
- This burning sensation is due to the increased levels of uric acid in the blood that has been crystallized, deposited and accumulated in the joint.
Low-Grade Fever and Fatigue
- Having a low-grade fever and fatigue when you have gout is often indicative of an acute attack.
- When this happens, the body’s natural response is to increase its temperature to fight off the infection, resulting in a low-grade fever.
If these symptoms are present, it’s important to seek medical attention, as gout can be effectively managed with the right treatment. However, gout in seniors can be easily misdiagnosed, so it’s vital to recognize the signs and symptoms of gout to receive the correct diagnosis and treatment.
Risk Factors Associated with Gout
Gout can be a major threat to the elderly population, and we’ve identified the most frequent risk factors. Fortunately, many of these risk factors can be managed with the right lifestyle choices which can reduce the risk of experiencing gout in seniors.
Genetics
When it comes to the elderly, it’s no surprise that genetics can play a major role in various health risks. Gout is one of those risks, and the fact that genetics can play a role in the developmnt of gout is a testament to how interconnected our bodies are. Studies have found that the most frequent risk factor of gout in seniors is genetic.
The condition is known to be hereditary, and those with a family history of gout are at a higher risk of developing it. Certain genetic patterns can influence uric acid levels in the body, which is one of the significant contributors to gout attacks.
Thankfully, knowing that genetics can play a role in an individual’s risk of gout can help guide decisions to reduce risks, like avoiding certain foods and beverages, or taking medications to reduce the pain and inflammation associated with gout attacks.
Certain Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can act as risk factors for gout in seniors. These conditions include chronic kidney disease, metabolic syndrome, hypertension, and diabetes.
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a long-term medical condition that occurs when the kidneys are not functioning optimally. In healthy individuals, the kidneys are responsible for removing metabolic waste and excess fluid from the body, as well as balancing electrolyte levels. CKD results in the impairment of these vital functions, leading to a build-up of uric acid in the body.
If left untreated, this buildup can cause severe medical issues, such as gout and even kidney failure. Symptoms of CKD can include fatigue, swelling, nausea, and a decrease in urine output. If you have any of these symptoms, it’s important to seek medical advice immediately to determine if CKD is the cause.
A metabolic syndrome is a group of conditions that include high blood pressure, high blood sugar, and an unhealthy balance of cholesterol. These conditions together can increase the risk of developing cardiovascular disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes and gout. It’s important to note that although metabolic syndrome is associated with an increased risk of developing certain conditions, it’s not a direct cause of any of them.
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a significant health concern that can cause a range of serious consequences for the body. One of the most common complications of hypertension is the strain it can put on the kidneys. When the kidneys are working too hard to filter out the blood, they can become overworked and unable to keep up with the demands.
This can lead to a buildup of uric acid in the body, which can cause several negative side effects. Not only can a buildup of uric acid increase the risk of kidney stones, but it can also cause joint pain and even gout in seniors.

Diet and Alcohol Consumption
Diet and Alcohol Consumption are two of the major risk factors when it comes to gout in seniors. The main dietary risk factor for gout in seniors is the consumption of purine-rich foods. These foods include:
- Beef, lamb, and venison are all types of red meat that are high in purine content, as well as organ meats.
- Kinds of seafood that are higher in purines, and should be eaten in moderation, including anchovies, herring, mackerel, sardines, trout, and tuna.
- Additionally, mussels, scallops, and shrimp also have higher levels of purines so it is important to keep track of how much you are consuming.
Alcohol consumption is also a risk factor for gout in seniors. Alcohol can increase the amount of uric acid in the blood, leading to an increased risk of gout.
Preventative measures to reduce flare-ups
An important component of managing gout in seniors is prevention. To prevent flare-ups, it’s advised to reduce inflammation and improve overall health. Some preventative measures to reduce flare-ups include:
- Maintaining an appropriate weight, as obesity is a risk factor for developing gout.
- Limiting alcohol intake, as alcohol increases the risk of gout attacks.
- Avoiding certain foods, such as those high in purines and fructose.
- Increasing physical activity, such as exercise, can help reduce uric acid levels in the body.
- Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water.
- Taking medications as prescribed by your physician.
- Diet and lifestyle changes
Diet and lifestyle changes are essential for managing gout in seniors. Foods rich in complex carbohydrates and plant proteins should be included in the diet, as well as foods high in calcium and vitamin C.
Additionally, alcohol and sugary drinks should be avoided. Exercise can also help reduce inflammation, and elderly patients should aim for 30 minutes of moderate physical activity most days of the week. Finally, managing stress can also help reduce gout flares, so relaxation techniques such as yoga or meditation can be beneficial.
Diagnosing and Treating Gout
Gout in seniors is a common form of arthritis that affects many elderly people. It’s especially prevalent in older individuals who have diabetes, hypertension, or a family history of gout. In such cases, the elderly are at a higher risk of developing painful gouty arthritis.
The diagnosis of gout in seniors is an important process that relies on combining the patient’s medical history, physical exam, laboratory tests, and imaging to determine the presence of gout and the most appropriate form of treatment. This process of detective work can sometimes be complicated, but when successful, it can lead to relief from the painful symptoms of gout in seniors and improved quality of life.
The medical history is important in determining if the patient has a family history of gout or if they have been exposed to certain environmental factors that may increase the risk of developing gout. The physical exam allows the clinician to examine joint swelling, pain, and other signs of gout. Laboratory tests provide an accurate diagnosis by measuring levels of uric acid in the body.
Medication Options
When it comes to treating gout in seniors, there are two primary medication options: Non-pharmacological treatments and Pharmacological treatments. Non-pharmacological treatments focus on lifestyle changes – including dietary modifications, weight control, and physical activity.

Non-pharmacological treatments
Non-pharmacological treatments are an incredibly important part of managing gout in seniors, as medications may not always be an option due to age or a preference to avoid them. Fortunately, these treatments focus on lifestyle modifications that can help the elderly manage their gout without resorting to medication.
Changes like reducing alcohol consumption, maintaining a healthy weight, and exercising regularly belong to the non-pharmacological treatments. So as eating a healthy, balanced diet and managing stress levels, which can also be beneficial. The elderly should always consult with their doctor before making any changes to their lifestyle, especially if they have any underlying health conditions.
Furthermore, there are also well-established dietary interventions, such as the Mediterranean Diet and other diets low in purines, that can be helpful. All of these interventions should be tailored to the individual’s preferences and capabilities.
Pharmacological Treatments
There are numerous medication options for effectively treating gout in seniors. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are an excellent choice for relieving pain and swelling associated with gout, while at the same time helping to limit uric acid production in the body. NSAIDs provide fast-acting, long-lasting relief and can be taken in the form of tablets or injections. Additionally, numerous other medications can be used to treat gout in seniors.
Colchicine is a groundbreaking drug that has helped countless individuals manage their painful conditions. It is often the go-to remedy for reducing inflammation and alleviating pain in the affected area. Put simply, it is an ideal solution for those suffering from gout, arthritis, and other chronic health problems.
With its powerful anti-inflammatory properties, this drug has been making a positive difference in people’s lives for decades. So if you’re looking for a reliable way to manage your health condition, you can’t go wrong with colchicine – it’s a proven performer that has helped countless individuals get their lives back on track.
Allopurinol is an amazing option that can help reduce the amount of uric acid in the body and prevent future flare-ups. This drug has been used for decades to successfully treat gout, and it’s a great way to reduce the amount of uric acid in the body. Allopurinol helps by blocking the enzyme that produces uric acid, thus reducing the levels in the body.
It’s a powerful drug that can make a huge difference in the lives of those who suffer from gout, so it’s definitely worth considering if you’re looking for a way to reduce your flare-ups. Additionally, it’s available in both tablet and liquid form, so you can find the best method of taking it.
Corticosteroids are a great way to reduce inflammation and provide relief from gout pain. They can be taken orally or they can be injected directly into the affected joint. Corticosteroids can start to provide relief quickly, and they are especially helpful if you are in a lot of pain.
They are also very effective at reducing the swelling of joints caused by gout. They are also very safe to use and have few side effects. So, if you are suffering from gout, talk to your doctor about trying corticosteroids to get relief and reduce inflammation quickly.
When it comes to taking any kind of medication, it’s always important to talk to your doctor about potential side effects and interactions. Don’t be afraid to ask questions and voice any concerns you may have about taking your medication. The more you know about the medication you are taking, the better off you will be.
Your doctor or pharmacist can provide important information about the potential side effects and interactions, so make sure to ask them if you have any questions. With the right information, you can ensure you are taking the best care of yourself and understanding the effects of your medication.
Wrapping It Up
To wrap it up, gout is a complex disease that can affect the elderly in a variety of ways. It is important to understand how gout can affect an elderly person’s quality of life and take the necessary steps to prevent its onset.
While there is no one-size-fits-all approach to managing gout, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing gout, such as maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress levels. Additionally, being aware of the individual risk factors that make an elderly person more likely to develop gout is essential in order to take the necessary steps to reduce their risk.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is the key to successful gout management for elderly individuals. Through proper medical monitoring, lifestyle modifications, and medications when necessary, seniors can greatly improve their quality of life and enjoy life to the fullest. Regular physical activity, a nutritious diet, and adequate hydration are essential.
Medications such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and uric acid-lowering medications can help to manage the symptoms of gout. Furthermore, monitoring is essential to ensure that the gout is under control and not causing harm to other parts of the body. Regular check-ups with medical professionals can help to identify any potential issues early, thereby preventing any further complications.
If you find this post helpful, you might also want to know the hobbies that can help you boost your retirement income.
Disclaimer
The content provided on MySeniors.World is for informational purposes only and is not intended as either financial or medical advice. Always consult a qualified professional before making any investment or health-related decisions.
Posts may contain affiliate links, meaning we earn a commission – at no additional cost to you, if you click through and make a purchase. Your support helps us continue providing valuable content.